Research topics - details
Images and models for
Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery
Project
Labex CAMI PhD Thesis
(2016-2019). Collaboration:
TIMC,
IMAG, Université Grenoble-Alpes. Staff:
Pablo Alvarez (Thesis, tel-03104312),
Simon Rouzé MD (Thesis, tel-03694901),
Yohan
Payan,
Matthieu Chabanas (co-supervisors TIMC).Project ANR TecSan VATSop (2020-). Collaboration: TIMC, IMAG, Université Grenoble-Alpes, MIMESIS, INRIA (Strasbourg). Staff: Pablo Alvarez (Post-Doc, Grenoble), Simon Rouzé MD, Valentin Boussot (Master Thesis, Thesis), Miguel Castro (Ing.), Tang Hui, Chen Qingmei (Master).
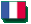
The objective is the intraoperative localization of pulmonary nodules in video-assisted thoracoscopy surgery (VATS).The main idea of our approach is to couple and integrate a biomechanical model of the lung to the image processing needed for guidance.
Localization of the nodule on intraoperative image. VATS procedure inducing in pneumothorax. Localization of the nodule in the deflated lung using a CBCT
Rouzé S., Alvarez P., Delatour B., Flécher E., Dillenseger J.-L., Verhoye J.-P., “Localisation de nodules pulmonaires en réalité augmentée grâce au Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) en vidéo-thoracoscopie”, Bulletin de l’Académie Nationale de Médecine, 202, 8-9, 2018, pp. 1897-1908, doi: 10.1016/S0001-4079(19)30183-9.
Alvarez P., Rouzé S., Miga M., Payan Y., Dillenseger J.-L., Chabanas M., “A hybrid, image-based and biomechanics-based registration approach to markerless intraoperative nodule localization during video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery”, Medical Image Analysis, 2021, pp. 101983, doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.101983
Estimation of lung deformities between dorsal and lateral decubitus positions.
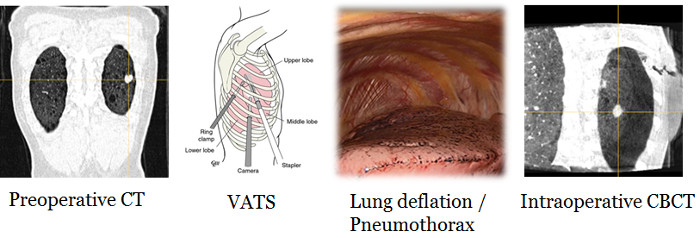
The preoperative volume is acquired in supine CT and the intraoperative volume is acquired in lateral CBCT. The idea is to analyse and estimate the deformations between these two modalities using elastic registration. In a second step, we try to predict these deformations by a statistical model.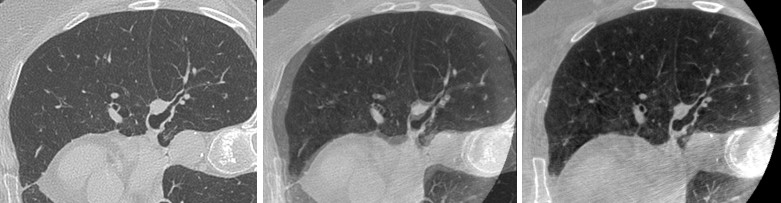
On the left: CT volume acquired in dorsal dcubitus position; On the right: CBCT volume acquired in lateral decubitus position; Midle: rigid registration of the 2 volumes
Alvarez P., Chabanas M., Rouzé S., Castro M., Payan Y., Dillenseger J.-L., “Lung deformation between preoperative CT and intraoperative CBCT for Thoracoscopic Surgery: a case study”, SPIE Medical Imaging: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, Houston, 2018, pp.S45-S46, doi: 10.1117/12.229393
Alvarez P., Chabanas M., Sikora S., Rouzé S., Payan Y., Dillenseger J.-L., “Measurement and analysis of lobar lung deformation after a change of patient position during video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery”, IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2022, doi: 10.1109/tbme.2022.3205458.
Boussot V., Dillenseger, J.-L., “Modèle statistique pour la prédiction de la déformation du poumon pendant la chirurgie thoracique vidéo-assistée“, RITS 2022, Brest, 2022.
Boussot V., Dillenseger J.-L., “Statistical model for the prediction of lung deformation during video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery”, SPIE Medical Imaging, Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, SPIE vol. 12466, San Diego, 2023, doi: 10.1117/12.2646983.
Biomechanical modeling of the deflation (collaboration Grenoble, Rennes)
Starting from the previous model, the idea is to develop a biomechanical model which simulates the deflation due to pneumothorax.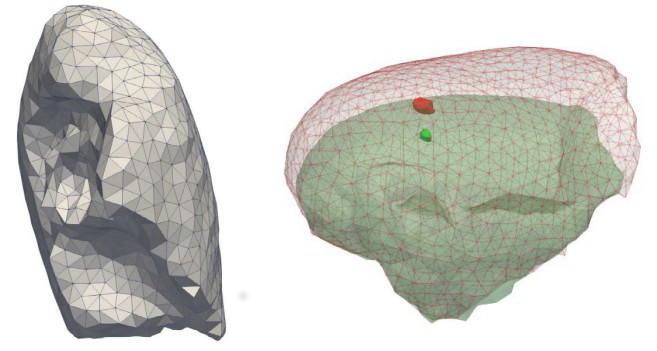
Lung mesh generation and deflation modeling
Alvarez P., Rouzé S., Chabanas M., Castro M., Payan Y., Dillenseger J.-L., “Modeling lung deflation during video-assisted thoracoscopy surgery for the localization of small nodules", EUROMECH Colloquium 595: Biomechanics and computer assisted surgery meets medical reality, Villeneuve d’Asq, 2017
Alvarez P., Rouzé S., Chabanas M., Castro M., Payan Y., Dillenseger J.-L., “A biomechanical model of lung deflation during VATS for the localization of small nodules”, Surgetica, Strasbourg, 2017.
Alvarez P., Narasimhan S. Rouzé S., Dillenseger J.-L., Payan Y., Miga M., Chabanas M., “Biphasic model of lung deformations for Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)”, IEEE ISBI 2019, Venise, 2019, pp 1367-1371, doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2019.8759219.
Lung segmentation
The biomechanical model must have a precise
anatomical description (vascular and bronchial tree and lung lobes) at
the preoperative stage (extracted from preoperative CT) and at the
intraoperative stage (CBCT). Lung segmentation in CT. We initially focused on the easier segmentation in CT, proposing a GAN-type architecture with U-Net model segmentation as generator (Chen Qingmei). However, more efficient methods such as TotalSegmentator have been developed in the literature.
Lung segmentation in CBCT. Secondly, in view of the difficulty of obtaining lower-quality CBCT images (truncated and noisy volumes), we adopted a strategy of style translation from CBCT to CT to benefit from efficient CT segmentation methods (V. Boussot).
We explored two AI models for transferring style from CBCT to CT: a GAN-based model and a model based on diffusion models (V. Boussot's mobility at CIRO, Australia). As both models are based on unsupervised learning, one of the key points is the accuracy and robustness of the registration (elastic or AI-based) between CBCTs and CTs from the same patient during training. We have developed a new semantic metric of similarity between two volumes called IMPACT. This metric is based on the similarity between deep layers of generic segmentation models (TotalSegmentator, Segment Anything - SAM- or other) in order to compare deep features. This metric has been tested on different organs and different acquisition modalities and brands (CT, CBCT, MRI, etc.) to demonstrate its generality and robustness, and has been integrated into both classic registration solutions (Elastix) and AI-based solutions (loss in VoxelMorph).

Impact of the similarity metric on CT registration on a CBCT image (left) using Elastix. Result after registration using the IMPACT metric (center) and Normalized Cross Correlation (NCC on the right).
Chen Q., Tang H., Dillenseger J.-L., “LLASN: Lung lobes segmentation using adversarial network”, IEEE 6th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Nanjing, 2021, pp. 240-244, doi: 10.1109/ICSIP52628.2021.9688972.
Hémon C., Boussot V., Texier B., Dillenseger J.-L., Nunes J.-C., “Guiding unsupervised CBCT-to-CT synthesis using content and style representation by an enhanced perceptual synthesis (CREPs) loss”, SynthRAD2023 Challenge, MICCAI 2023, Vancouver, 2023.
Boussot V., Hémon C., Nunes J.-C., Downling J., Rouzé S., Lafond C., Barateau A., Dillenseger J.-L., “IMPACT: A generic semantic loss for multimodal medical image registration”, arXiv:2503.24121, 2025.
Augmented Reality (Collaboration Grenoble, Rennes)
The aim is to reproject the position of the nodule estimated on the interventional CBCT onto the endoscopic camera view. This part is essentially carried out by our collaborators in Grenoble (S. Voros, M. Chabanas, B. Noblet). Our role was to propose a classical calibration of a 3D endoscope based on CharUco grids (R. Coercio) and to propose an automatic segmentation of anatomical structures (ribs) or surgical structures (Alexis Retractors) common to the CBCT and the endoscopic view (W. Tam, T. C. Luong)
Top: Segmentation of ribs and Alexis in the video image using YoloV8 (W. Tam)
Bottom: CBCT segmentation of Alexis using a curvature-based technique (T.C Luong)
Coércio R M. A., Farias A.R., Dillenseger J.-L., “Camera calibration algorithm for lung nodule detection in videolaparoscopy”, 24th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Athen, 2024, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/isbi56570.2024.10635152
Tam W., Dillenseger J.-L., Babyn P., Alirezaie J., “Rib segmentation in surgical images for Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery“, IEEE CBMS 2024, Guadalajara, 2024, pp. 450-455, doi: 10.1109/cbms61543.2024.00080
Luong T C., Dillenseger J.-L., “Segmentation of Alexis retractors in the context of augmented reality in Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery”, SPIE Medical Imaging 2025: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, 2025, doi: 10.1117/12.3044346.
2D-3D Deformable registration (MIMESIS, Strasbourg)
The idea is to estimate the 3D deformation field in a volume from a single fluoroscopic image. In his thesis, F. Lecomte (supervised by S. Cotin and co-supervised by J.-L. Dillenseger) solves this inverse problem using an AI network trained on synthetic data (simulated radiography on CT scan volumes undergoing displacement fields).Lecomte F., Verde J., Dillenseger J.-L., Cotin S., “Domain agnostic 2D-3D deformable registration. Application to fluoroscopic guidance without contrast agent”, Medical Image Analysis, 2025, 103688, doi : 10.1016/j.media.2025.103688.
Lecomte F., Alvarez P. Cotin S., Dillenseger J.-L. “Beyond respiratory models: a physics-enhanced synthetic data generation method for 2D-3D deformable registration”, IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, 2024, pp. 2413-2421, doi: 10.1109/cbms61543.2024.00080.
Lecomte F., Scarponi V., Alvarez P., Verde J., Dillenseger J.-L., Vibert E., Cotin S., “Enhancing fluoroscopy-guided interventions: a neural network to predict vessel deformation without contrast agents”, 15th Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics, Londres, 2023, doi: 10.31256/hsmr2023.38
Fall detection using stereoscopic thermal cameras or coupled thermal/depth cameras
Project ANR TecSan PRuDENCE (2016-2019). Collaboration : NeoTec Vision (Pacé), ECAM Rennes - Louis de Broglie (Bruz), Living Lab Activ Ageing UTT (Troyes), équipe accueil EA 2694 (Lille). Staff : Yannick Zoetgnandé (Thesis, tel-03118117), Imen Halima (Thesis ECAM Rennes, tel-03212630), Soumaya Msaad (Thesis supervised by Guy Carrault, tel-03815836), Abderamane Abakar Bechir (Master), Mathis Fleury, Cédric Moubri-Tournès, OscarTanguille (ESIR training period).One of the goals of this project is the fall detection of elderly people by either a pair of stereoscopic low resolution thermal cameras or the coupling of a depth and a thermal camera.
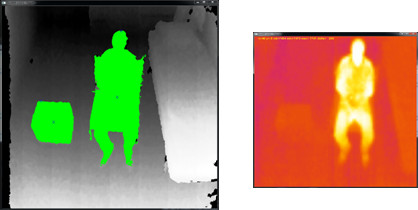
Depth and thermal images
Lan Hing Ting K., Voilmy D., Dessinger G., Gauthier V., Dillenseger J-L., Carrault G., Laferté J-M., Fougères A-J., “Co-designing a falls detection device: combining concerns for human motion and elders needs”, Workshop Visual user interfaces for human motion, ACM AVI 2020, 2020.
Lan Hing Ting K., Voilmy D., Dessinger G., Gauthier V., Dillenseger J-L., Carrault G., Laferté J-M., Fougères A-J., “Causes et conséquences de la chute : les comprendre pour informer la conception d’un dispositif de prévention”, Colloque francophone sur la chute de la personne âgée, Valenciennes, 2021.
People tracking and activity recognition by coupling a depth and a thermal camera
The tracking of people is performed on a pair of images (depth sensor / thermal image) by a particle filter approach or by deep learning (Imen Halima).Particle filter and 2 tracking results using the fusion of information from depth sensor and thermal image
Halima I., Laferté J.-M., Dillenseger J.-L., Cormier G., Fougères A.-J., "Sensors fusion for head tracking using Particle filter in a context of falls detection”, 1st International Conference on Advances in Signal Processing and Artificial Intelligence (ASPAI' 2019), Barcelona, 2019,pp. 134-139.
Halima I., Laferté J.-M., Cormier G., Fougères A.-J., Dillenseger J.-L., “ Depth and thermal information fusion for head tracking using particle filter in a fall detection context”, Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, 27, 2, 2020, pp. 195-208, doi: 10.3233/ICA-190615.
We addressed activity tracking by deep learning. For this we created a learning base of activities on 3 different sites (an empty room, an apartment in a living lab and a real apartment) with 3 different people. We trained an SSD network to estimate 4 postures (sitting, standing, lying on the bed and lying on the floor) (Imen Halima).
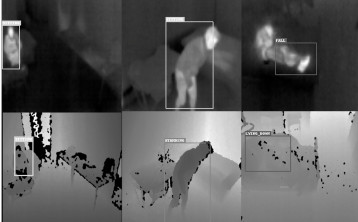
Activity recogintion fron thermal and depth cameras
Fall detection of elderly people by either a pair of stereoscopic low resolution thermal cameras
Thermal cameras stereo calibration and subpixel reconstruction
The chosen thermal sensors (Lepton 2 FLIR) are low price but also has a very low resolution (80x60 pixels). We built a car-bulbs calibration grid adapted to thermal imaging cameras (Mathis Fleury, Cédric Moubri-Tournès, Oscar Tanguille). We have also developed a robust low resolution stereo-camera calibration framework (Yannick Zoetgnandé).The image content and low resolution of the sensors have also an impact on the reconstruction of the scene by stereoscopic vision. We have developed a reconstruction protocol based on the robust extraction of visual features by phase congruency, feature matching and sub-pixel precision disparity estimation by phase coherence (Yannick Zoetgnandé).
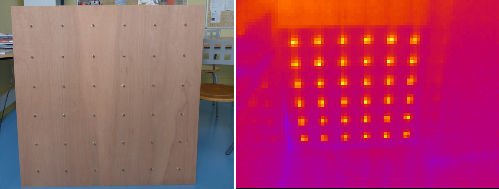
Calibration grid and view from one of the thermal camera
Zoetgnandé Y., Fougères A.-J., Cormier G., Dillenseger J.-L., “Robust low resolution thermal stereo camera calibration”, 11th International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2018), proc. SPIE 11041, Munich, 2018, pp. 11041-1D, doi: 10.1117/12.2523440 .
Zoetgnandé Y., Fougères A.-J., Cormier G., Dillenseger J.-L., “Sub-pixel matching method for low resolution thermal stereo images”, Infrared Physics and Technology, 105, 2020, pp. 103161, doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2019.103161.
Thermal Images super-resolution
The goal is the improvment of the thermal images resolution by a ratio 3 or 4. we develloped a CNN-based approach with edge salliency (Yannick Zoetgnandé during an exchange at Ryerson University, Toronto, Canada, MITACS Globalink Research Award FR26353, collaboration with Pr Alirezaie,).
Original image 80x60 (3X zoom) - image 320x240 obtained afetr bilinéar interpolation - image 320x240 obtained by our CNN-based approach with edge salliency
Zoetgnandé Y., Dillenseger J.-L., Alirezaie J., “Edge focused super-resolution of thermal images”, International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, 2019, doi: 10.1109/IJCNN.2019.8852320.
Fall detection by ground points learning
Despite the sub-pixel accuracy, the classical stereoscopic reconstruction did not allow an accurate reconstruction of the scene, in particular the ground plane and the person (0.5 m of uncertainty in depth). We therefore opted for a solution without calibration, where a system learns to classify points in space as belonging to "ground/not ground" (either by SVM or by deep learning). Then, from a stereo-thermal image pair, the device extracts and matches visual features of the person and estimates whether these features are on the ground or not. This allows to detect or not a fall (Yannick Zoetgnandé).Zoetgnandé Y., Dillenseger J.-L., “A generic interpretable fall detection framework based on low-resolution thermal images”, Journées de la Recherche en Informatique au Burkina Faso (JRI-2021), Bobo Dioulasso, 2021, 13 pages, doi: 10.4108/eai.11-11-2021.2317972.
Detection of activities by transfer learning
We also tried to estimate the activity of elderly people (walking, crawling, sitting and falling, lying down and falling, etc.) from a single low resolution thermal camera.As we did not have enough data for training, we explored several solutions where the training of a network performed on anotated RGB data was used to process the thermal data from our camerasZoetgnandé Y., Dillenseger J.-L., “Domain generalization for activity recognition: Learn from visible, infer with thermal”, 11 th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods, 2022, pp.722-729, doi: 10.5220/0010906300003122.
Prevention of falls and estimation of the frailty of elderly people by monitoring activities.
The objective is to recover the activities of the elderly person recognized by the previous techniques and to make a longitudinal follow-up and to extract statistics aiming at measuring the degree of frailty of the person (Soumaya Msaad).Msaad S., Dillenseger J.-L., Cormier G., Carrault G., “Detection of changes in the behaviour of the elderly person”, IEEE-EMBS, Guadalajara, 2021, pp. 6995-6998, doi: 10.1109/embc46164.2021.9630971.
Msaad S., Dillenseger J.-L., Carrault G., “Interest of the minimum edit distance to detect behaviour change of the elderly person”, IEEE-EMBS, Guadalajara, 2021, pp. 7377-7380, doi: 10.1109/embc46164.2021.9629665.
Msaad S., Zoetgnandé Y., Dillenseger J.-L., Carrault G., “Detecting change in the routine of the elderly”, Measurement: Sensors, 2022, pp. 100418, doi: 10.1016/j.measen.2022.100418.
Dillenseger J.-L., "Visualisation Scientifique en médecine. Application à la visualisation de l'anatomie et à la visualisation en épileptologie clinique", Habilitation à Diriger des Recherches, Juin 2003.
Evaluation of 3D visualization tools
Taxonomy of quality evaluation methods in 3D medical visualization. Evaluation of the influence of the visual coding scheme: size scale. Collaboration : Beatriz Souza santos (Univ Aveiro, Portugal).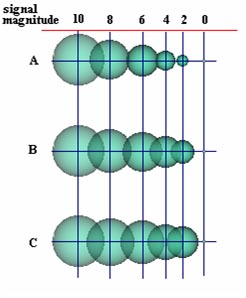
Sousa Santos B., Dillenseger J.-L., "Quality evaluation in medical visualization: some issues and a taxonomy of methods", Medical Imaging 2005: Image-Guided Procedures and Display, San Diego, Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 5744, Feb. 2005, pp. 612-620.
Sousa Santos B., Dillenseger J.-L., Ferreira C., "Experimental Methodology for the Evaluation of the 3D Visualization of Quantitative Stereoelectroencephalographic Information", Journal of Computing and Information Technology, 10, 2, 2002, pp. 93-103.
Multi-purpose ray casting
Combination of primitive image processing algorithms operating along the rays during visualization.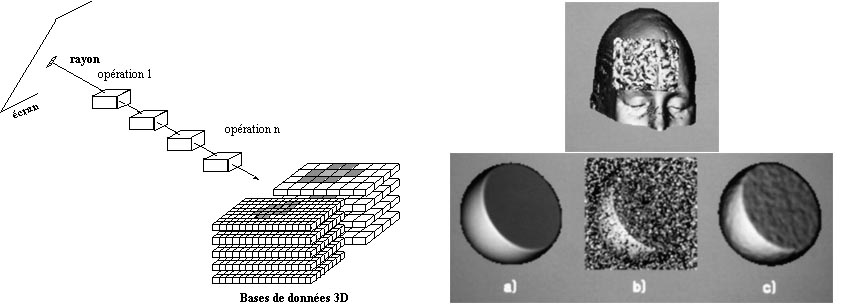 Principle
- segmentation during visualization- noise canceling during
visualization
Principle
- segmentation during visualization- noise canceling during
visualizationDillenseger J.-L., Hamitouche C., Coatrieux J.-L., "An Integrated Multi-purpose Ray Tracing Framework for the Visualization of Medical Images", proc. IEEE-EMBS, Orlando, Nov. 1991, pp. 1125-1126.
Dillenseger J.-L., "Imagerie Tridimensionnelle Morphologique et Fonctionnelle en Multimodalité", Thèse de l'Université François Rabelais, Tours, Décembre 1992, Directeur de Thèse : Jean-Louis Coatrieux.
Multi-Agent Knowledge-Based Ray Tracing
Intégration of specific knowledge during visualization.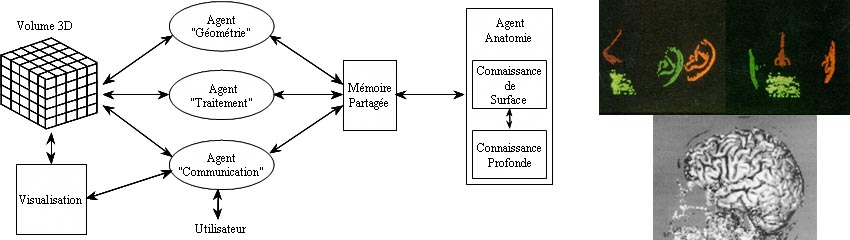 Multi-Agent
frame. Automatic prepositionning from facial feature labeling. Cortex
segmentation using knowledge on the acquisition modality and the
morpohological properties
Multi-Agent
frame. Automatic prepositionning from facial feature labeling. Cortex
segmentation using knowledge on the acquisition modality and the
morpohological propertiesDillenseger J.-L., Le Merrer M.-A., Haigron P., Garreau M., Coatrieux J.-L, "Modèle de connaissance et lancer de rayons pour le traitement d'images volumiques multimodales", Innov. et Tech. en Biol. et Med., 16, 1, 1995, pp. 1-11.